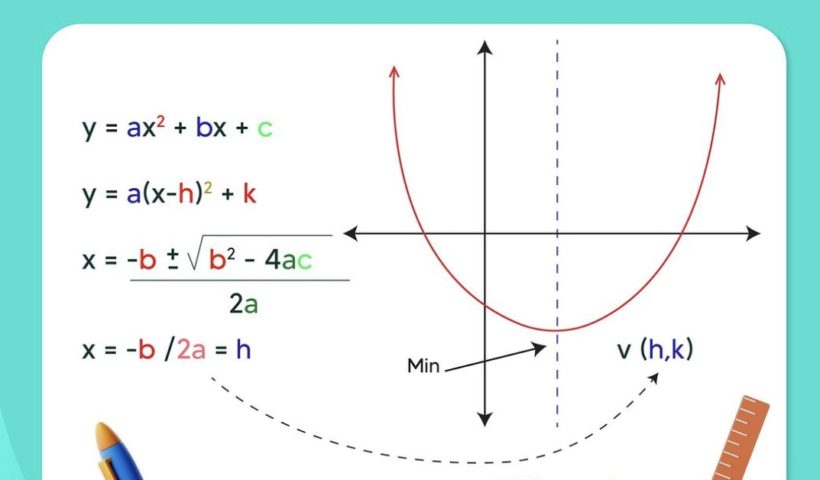
[Please watch the video attached at the end of this blog for a visual explanation on Master Quadratic Functions] Quadratic functions are generally given in…
View More Master Quadratic Functions | Cambridge IGCSE MathematicsAuthor: Kulni Gamage
Beyond Perception: Exploring the Secrets of Organism Size | Cambridge IGCSE Biology
[Please watch the video attached at the end of this blog for a visual explanation on Beyond Perception: Exploring the Secrets of Organism Size] Topic…
View More Beyond Perception: Exploring the Secrets of Organism Size | Cambridge IGCSE BiologyMastering Basic Differentiation Rules | Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics
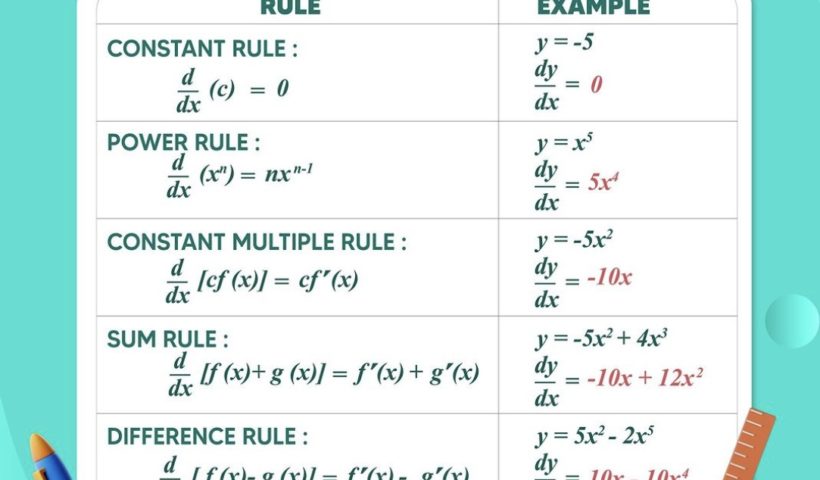
[Please watch the video attached at the end of this blog for a visual explanation on Mastering Basic Differentiation Rules] Differentiation is a key lesson…
View More Mastering Basic Differentiation Rules | Cambridge IGCSE MathematicsUnveiling the Secrets of Specialized Plant Cell Structure and Functions! | Cambridge IGCSE Biology
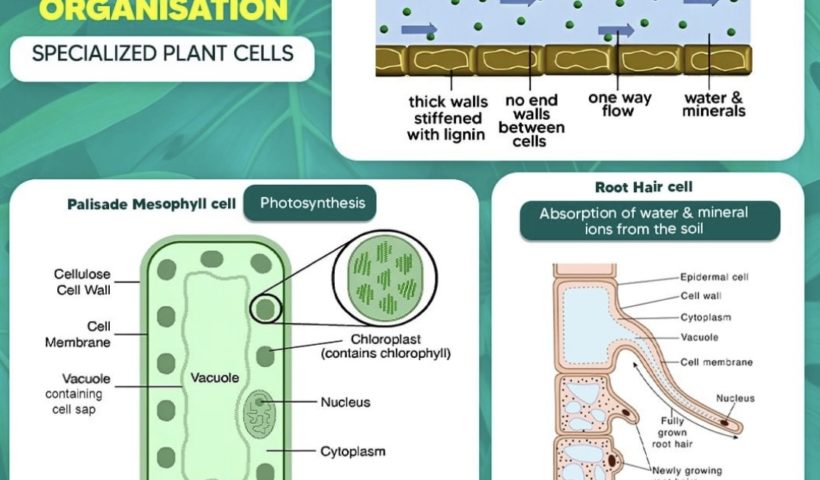
Unveiling the Secrets of Specialized Plant Cell Structure and Functions In one of the previous videos, we learned about the basic plant cell and the…
View More Unveiling the Secrets of Specialized Plant Cell Structure and Functions! | Cambridge IGCSE BiologyUnveiling the Wonders of Specialized Animal Cells & Functions| Cambridge IGCSE Biology
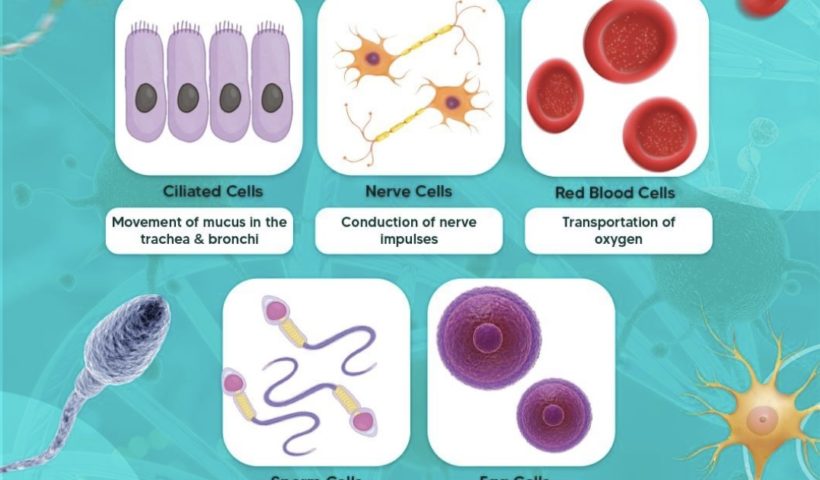
[Please watch the video attached at the end of this blog for a visual explanation of the Unveiling the Wonders of Specialised Animal Cells &…
View More Unveiling the Wonders of Specialized Animal Cells & Functions| Cambridge IGCSE Biology